YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCcwnTKWxSlkv_iarGQ_zbPg/featured
Instagram:
https://www.instagram.com/?hl=en
Facebook:
https://www.facebook.com/Creative-ideas-EEE-110709481470623/?ref=pages_you_manage
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCcwnTKWxSlkv_iarGQ_zbPg/featured
Instagram:
https://www.instagram.com/?hl=en
Facebook:
https://www.facebook.com/Creative-ideas-EEE-110709481470623/?ref=pages_you_manage
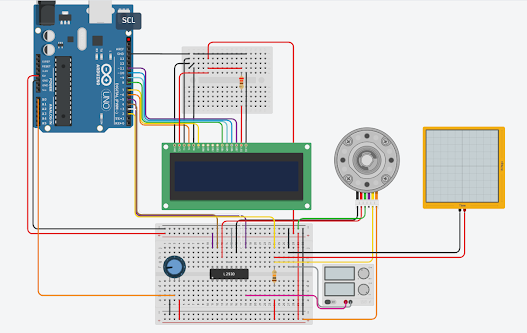
The project maintains the temperature of a room in [20, 25] degree Celsius.
Weather changes become hard to adapt. That is, during Winter we face difficulties tolerating the freezing cold, and that is why people often prefer wearing coats during the season. On the other hand, the weather becomes too warm in summer. Thus, having understood the switching operation of transistors, unidirectional current flow in diodes, the principle of operation of motors, the resistance from resistors combined with the transformation capability of the transducer, the temperature sensor in this case, I would like to summarize the operation of my project as follows.
1. If the temperature exceeds the maximum of the aforementioned "desired" range, then the LCD displays that the temperature is higher and informs the FAN to turn on. Then the FAN starts its rotation/vibration, and after a while, the temperature gets lowered falling in the range, then the LCD commands the FAN to turn off.
2. Whenever the sensor's temperature reading goes down below the possible minimum temperature in the range, the LCD notifies that the temperature is LOWER and tells the heater to be turned on, and after the temperature is in the range, it displays that temperature is OK and orders the heater to be switched off.
3. The last condition is whenever the temperature is within the desired range, the LCD tells that the temperature is normal. Thus, it asks to turn off everything. This condition can, for instance, be observed if you run the code and the slider's position remains unchanged. That tells one that the default slider position is within the desired room temperature range (i.e. the default is 24.78 degree C).
Likewise, system iterates forever unless it gets terminated by the user due to the behavior of the loop ( ) function.
Arduino Code: Click Here
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCcwnTKWxSlkv_iarGQ_zbPg/featured
Instagram:
https://www.instagram.com/?hl=en
Facebook:
https://www.facebook.com/Creative-ideas-EEE-110709481470623/?ref=pages_you_manage
Just as you’ve learned from start by wiring up your Arduino and breadboard with power and ground next to the example circuit, then add the the three red LEDs to the breadboard, as shown. These will be the "bar graph" lights for visually indicating the sensor's distance measurement.
Drag an Arduino Uno and breadboard from the components panel to the workplane, next to the existing circuit.
Connect the 5 volt and ground pins on the Arduino to the power (+) and ground (-) rails on the breadboard with wires. You can change the wire colors if you want to! Either use the inspector dropdown or the number keys on your keyboard.
Drag three LEDs on the breadboard in row E, spaced 2 breadboard sockets apart. You can change the LED color using the inspector that pops up when you click on each one.
Use a 220 Ohm resistor to connect each LED's cathode (left leg) to the ground rail (black) of the breadboard. You can change a resistor's value by highlighting it and using the dropdown menu.
Connect the LED anodes (right legs) to digital pins 4, 3, and 2 on the Arduino. The LED anode (+) is the terminal that current flows into. This will connect to the digital output pins on the Arduino. The cathode (-) is the terminal that current flows from. This will connect to the ground rail.
Let's measure distances with an ultrasonic rangefinder (distance sensor) and Arduino's digital input. We'll connect up a circuit using a breadboard and use some simple Arduino code to control a single LED.
You may have already learned to read a pushbutton and PIR motion sensor with Arduino's digital input, and we'll build on those skills in this lesson.
Ultrasonic rangefinders use sound waves to bounce off objects in front of them, much like bats using echolocation to sense their environment. The proximity sensor sends out a signal and measures how long it takes to return. The Arduino program receives this information and calculates the distance between the sensor and object.

Find this circuit on Tinkercad
Explore the sample circuit embedded here by starting the simulation and clicking on the proximity sensor. This will activate a highlighted area in front of the sensor with a circle "object" inside. You may need to resize the view if the circle is off screen.
Click and drag the "object" circle closer and further away, noticing the changing distance values on screen. More LEDs will light up the closer you get to the sensor.
I was using a normal LCD for this project before and then I need to add few sensors in this setup which need more digital pins, so I replace the LCD with a LCD which got I2C board soldered on it.
Thanks UTSOURCE.net to offer electronic components for this project!
they deal in all kinds of electronic components, for example, Arduino board, Ultrasonic sensor, and many more.
watch the tutorial on my channel
Be very careful connecting the circuit. Check your work, and it helps to work with a Buddy. Have one person looking at the schematic, and one looking at the circuit. Sometimes it is easier to get it right working in pairs.
Now the objective of this project is to measure distance using the ultrasonic sensor, and then display that value on the LCD display. You should have the skills you need from the earlier lessons. Try and do this project on your own, but if you get stuck, you can look at my code below. As always, don’t copy and paste my code, but it should be used as a guide to help you write yours if you get stuck.
our assignment is to get this project going, and show that you can measure distance and then display it on the LCD. After showing me your work, then you need to take the project in your own unique direction. What can you make based on what you have learned in the last few lessons. You should use some combination of Ultrasonic Sensor, LCD, and Servo to make a project or product or your own invention. You have the technical skills, you have the equipment, now go be creative!
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCcwnTKWxSlkv_iarGQ_zbPg/featured
Instagram:
https://www.instagram.com/?hl=en
Facebook:
https://www.facebook.com/Creative-ideas-EEE-110709481470623/?ref=pages_you_manage
One of the greatest things about DIY maker electronics is transforming small, cheap parts into fun and interesting finished projects. Even a 16x2 character 5V LCD screen that is usually used with an Arduino for the simplest of text-based displays (for example: numeric sensor readings) can be utilised in a fascinating way.
Attend our workshop this week to learn how to use this limited setup to make a graphics-based game. We’ll use an Arduino and the LCD screen to create a side-scrolling jumping game with a one-button control. For the next step, we’ll port it into a compact prototype.
Prerequisites
- All hardware materials (including Arduinos, LCD screens, pushbuttons etc) will be provided
- Bring your laptop
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCcwnTKWxSlkv_iarGQ_zbPg/featured
Instagram:
https://www.instagram.com/?hl=en
Facebook:
https://www.facebook.com/Creative-ideas-EEE-110709481470623/?ref=pages_you_manage
RESISTOR
What is Resistor?
Ø Resistor is One of the Electronic's Main Components
and the Resistor is Called a Passive Components.
Ø The Work of this resistor is to
Limit the Currents Flow in the Circuits.
Ø For Example, take one Tupping and
Pass the High Flow Rate Water into the Tupping and have to be Control the Flow
of water so What we will to there to control the Flow can be Connect the Valve
to control the Flow of Water Similar in Electronics Circuits There is a High Current
in the Path To control the Current We can Use the Resistor.
Ø Instead of valve we are using here
Resistor.
Ø To choose the Resistor we must be
known About OHM Law as well as know about Current and voltage in the circuits
Ø The Resistance is measured in OHMS.
What the
resistor will do in a Circuits?
Ø The Resistor can work like a potential
divider.
Ø The Resistor can work like a Biasing
Resistor.
Ø The Resistor can work like a Op Amp-Feedback.
Ø The Resistor can work like a Current
Limiting
Ø The Resistor can work like a Impedance
Matching
Ø The Resistor can work like a Current
Measuring
Ø The Resistor can work like a Data and
Address pullups.
What is Potential
Divider?
Ø The Potential Divider two or more
resistor is connected in a series from that we can take a multiples voltage that
is called as a Potential Divider.
Ø If the resistor is connected in a
Parallel then there is a current Divider
What is
Biasing Resistor?
Ø The Biasing Resistor is Transistor
and many other devices need to have AC and DC operating characteristics and
gain values set up for correct operation. This is Done with multiple resistors
and is often called biasing.
What is Op
Amp – Feed back?
Ø Most op-amp circuits need to have their gain and
feedback functionality set by resistors external to the amplifier chip;
resistors are the primary means of doing this
What is Current
Limit?
Ø Resistors can be used to limit the
amount of current that flows in a circuit element. This is a useful safety
function in many circuits limiting the current that can flow into an LED to
manage its brightness
What is Impedance
Matching?
Ø To maximize power transmission at
high frequencies the impedance of the receive and transmit ends of a circuit
need to be the same. Resistors can perform at least part of this requirement
What is
current measuring?
Ø Many circuits need to know how much
current is flowing, however, it is much easier to measure voltage, so inserting
a resistor into the circuit to ‘develop’ a voltage – remember Ohm's law- is a
common technique for measuring current
What is Data
and Address pullup?
Ø This functionality helps to reduce
noise issues on high-speed computer busses. When a data bus tri-states or is
driven high, it is often necessary to pull it into a known state or to make
sure its output high is well above the switching point of other logic elements
on the bus, and a pull up helps to do this
Type of Resistor?
Ø Fixed Value Resistors
What is Resistive
Materials?
What is Resistor
Specifications?
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCcwnTKWxSlkv_iarGQ_zbPg/featured
Instagram:
https://www.instagram.com/?hl=en
Facebook:
https://www.facebook.com/Creative-ideas-EEE-110709481470623/?ref=pages_you_manage
How to control dc motor with encoder: Arduino DC Motor Speed Control with Encoder- I have been using different types of stepper motors, Ser...